






- Stock: In Stock
- Model: Beta Arbutin
- SKU: 497-76-7
Available Options
Arbutin is commercially used as a skin-whitening agent in the cosmetic industry. It works by competitive inhibition of the enzyme, tyrosinase, a key enzyme in the synthesis of melanin.
Depending on the spatial structure of the glycosidic linkage between glucose and hydroquinone, arbutin forms two epimers: Alpha Arbutin and Beta arbutin.
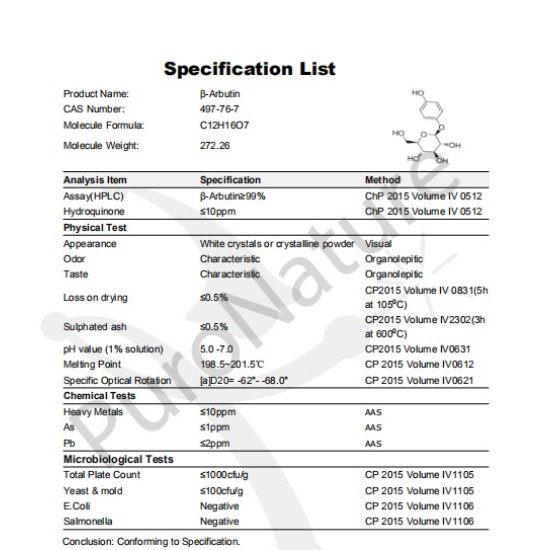
β-Arbutin 497-76-7
Beta Arbutin is often referred to as just Arbutin. It can be naturally extracted from plants such as bearberry and synthesized by chemical method. Synthesized Beta-Arbutin is currently one of the most widely used hypopigmented agents in cosmetics, while plant-derived drugs containing Beta Arbutin were initially used for the treatment of urinary tract infections, cystitis, kidney stones, and as diuretics in the medical field.
Arbutin exhibits potent melanin-inhibiting properties and confers whitening effects on the skin. Sun damage and injury or inflammation to the skin from acne, eczema or psoriasis are the two main factors that cause melanin production on the skin. Arbutin can reduce the accumulation of pigment by inhibiting the production of melanin, which accumulates on the skin when tyrosine is oxidized. An enzyme called tyrosinase is the catalytic for this reaction. Scientists found arbutin has shown inhibitory actions against tyrosinase. When topically applying skincare products containing Arbutin, the inhabitation of tyrosinase results in the decrease of melanin, thus, a whiter complexion.
Hyperpigmentation in the epidermis is caused by excessive melanin synthesis due to UV irradiation, wound or stress. Tyrosinase is one of the key enzymes involved in melanin synthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the first two steps in melanin synthesis: the hydroxylation of tyrosine to DOPA and the oxidation of DOPA to dopaquinone. Arbutin has a direct inhibitory function against tyrosinase, which leads to the prevention of melanin formation and a whitening effect on the skin.

-250x250.jpg)








